Data Center: How much energy does a stream consume?
NDC-GARBE 03/09/2024
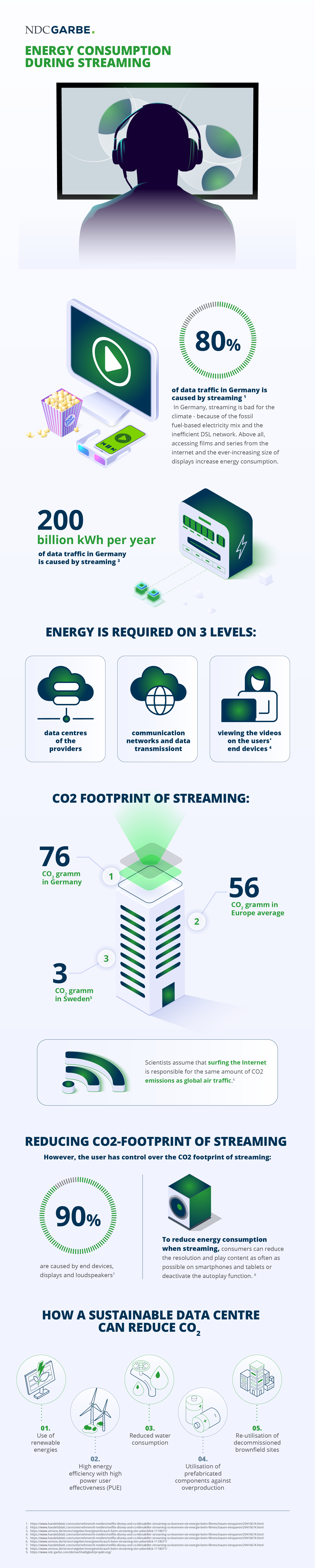
In recent years, streaming films and series has experienced an enormous boom, including here in Europe. However, this increase is also accompanied by an increased burden on the climate. According to experts, the operation of streaming services accounts for a significant proportion of global data traffic, around 80 percent in Germany, and therefore contributes significantly to energy consumption on the internet. According to studies, current internet consumption accounts for around 20 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions and this figure is set to rise to 50 percent by 2030.
Climate impact of streaming
The climate impact of streaming varies – in Germany it is high compared to other European countries due to the high proportion of fossil fuels in the electricity mix and inefficient DSL networks. A single movie night may leave a small carbon footprint, but the increasing use of streaming services and the change in viewing habits towards larger data volumes and screens have led to a significant increase in energy requirements and greenhouse gas emissions. The European average is 56 grams of CO2 emissions per hour of video streaming, with 76 grams of CO2 in Germany and 3 grams of CO2 in Sweden.
Specifically, the energy requirements of video streaming depend on the streaming provider and the end devices. Streaming providers are now increasingly trying to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions through more efficient compression processes – which already saved Netflix half of its previous energy consumption between 2015 and 2020 – shorter transmission paths and the use of renewable energies. Data center operators also have a responsibility to make data processing as sustainable as possible through sustainable construction, the use of renewable energy and the reuse of waste heat.
Consumption of CO2 emissions during streaming lies with the consumer
However, according to a study by the Carbon Trust, the greater responsibility for the CO2 emissions from streaming lies with the consumer, as streaming devices, loudspeaker boxes and Wi-Fi connections are said to account for around 90 percent of emissions. Consumers themselves have a major influence on energy consumption via screen size, resolution quality and choice of LAN cable or Wi-Fi. According to studies, 4K picture quality requires three times as much energy as HD streaming, while 720p picture quality consumes only a quarter of the energy required by 4K. According to this study, the main responsibility lies with the end consumer, but a contribution to sustainable streaming can be made at country level, for example through the large-scale sustainable expansion of the network.
Reducing CO2 emissions from the data center operator’s perspective
Overall, it is important that all players in the streaming industry work together to reduce energy consumption and find sustainable solutions. This is the only way to make streaming more environmentally friendly in the long term. As a data center developer, we are doing our part to reduce the ecological footprint of our data centers. We stand for efficient and sustainable development and pay attention to energy and water consumption throughout the process and focus on reducing embodied carbon.
For more information on how a data center can be built ESG compliant, see our interactive map.